Heap Tree
用 Tree 了解他,用 Array 實作相關的 operation
從 Binray Tree 的觀念出發,首先將原本 Tree 的 node 加上 Key (檢索鍵),如下:


key:priorityor weights or othersdata: original data (like:todo)
有分:
Min Heap(最小堆積):A min heap is a complete binary tree that is also a min tree.
Max Heap(最大堆積):A max heap is a complete binary tree that is also a max tree.
又稱
complete binary max tree)
概念類似 priority queue (heap on array)。
以下假設為沒有 priority queue 的年代, 用 Tree 的特性來設計 priority queue。
設計思路
- 需求: 最大的 Key 可以很快被找到
- 限制: 使用 Binary Tree 來實現
- 目標:
Max Heap/ priority queue, 降序 descending)
可簡單分為3個步驟1個限制:
- 把最大的放在 root
- 如何很快的找到下一個最大的值 (繼承人)
這兩步驟為第一步的設計,又被稱為
binary max tree。
- 用 Complete Binary Tree 來壓 tree 的高度
- 限制:
先維持 complete binary tree 的性質
要求 tree 的長相,稱為
complete binary max tree
各步驟詳細如下面介紹。
1. 把最大的放在 root
想法: 就直接把 Key 最大的放在 root。如下圖:

Exmaple:
14
/ \
6 8
/ \ / \
12 5 7 9
問題: 當把目前最大的 14 拿到後,需 traversal 剩下的所有 node 後,才能得到下一個最大的 node: 12
=> 超花時間
2. 如何很快的找到下一個最大的值 (繼承人)
Subtree 的 root 也都分別各自 subtree 中最大的 (sub-largest),如下圖:

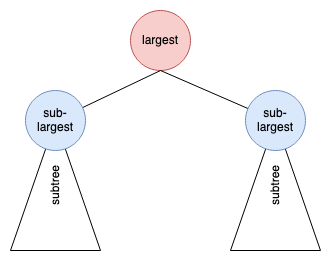
當 largest 被拿走後,就是兩個 subtree 的 sub-largest 比較一下就知道下一個是誰要補位上去。
Example:
14
/ \
12 9
/ \ / \
6 5 7 8
Binary Max Tree
上面兩步驟為第一步的設計,其又被稱為binary max tree。
root key >= other node's keyevery subtree is binary max tree
操作步驟如下:
14
/ \
12 9
/ \ / \
6 5 7 8
Get Largest: root, 14
Remove Largest and get sub-largest
12 跟 9 比大小,但因為 12 補上去了, 他的那個 subtree 也要再補一個 sub-largest
=> 6 跟 5 比較,6上去補位
12
/ \
6 9
\ / \
5 7 8
如此循環下去。
replace with largest of sub-root recursively
Worst time complexity
如果遇到 tree 是 skewed binary tree (歪斜樹) 時,
- time complexity O(h):
O(n)
50
/
48
\
30
/
21
\
10
/
3
binary max tree maintain 時要花很大力氣。
下一個思考思路就是:
-> 壓低 tree,讓 time complexity O(h) 從 O(n) 變為 O(log n)
3. 用 Complete Binary Tree 來壓 tree 的高度
要求 tree 的長相,稱為 complete binary max tree
不用 perfect (full) binary tree 的原因是因為 node 數量都是奇數
我們要如合結合 complete binary tree 與 binary max tree 呢?
Example:
14
/ \
12 9
/ \ /
4 8 5
Get Largest: root, 14
Remove Largest and get sub-largest
12 跟 9 比大小,但因為 12 補上去了, 他的那個 subtree 也要再補一個 sub-largest
=> 8 跟 4 比較,8上去補位
12
/ \
8 9
/ /
4 5
Note: 可能會想說把 5 往左移。但如果不是 5 是 8.5 呢?
這樣變成不是 complete binary tree 了, 事情變麻煩了,不好做。
換個思路思考!
先維持 complete binary tree 的性質
缺位時,先維持 complete binary tree 的性質
當 remove node 時,先讓最尾把的 node 補上來
=> 維持 complete binary tree
然後再讓 root 去跟 sub-largest 去比。
Example:
14
/ \
12 9
/ \ /
4 8 8.5
先讓最尾把的 node 補上來:
8.5
/ \
12 9
/ \
4 8
然後再去跟 sub-largest 比:
12
/ \
8.5 9
/ \
4 8
然後 8.5 再去跟他的 sub-tree 去比,如此循環。
結論
Complete binary max tree 就是一般所稱的 Max Heap。
操作步驟如下:
Remove:
1. move last node to root (complete binary tree)
2. sink down to keep binary max tree
time complexity: O(log n)
Insertion node
如果要新增 node,一樣先插在最後面,維持 complete binary tree,再去檢查 binary max tree 性質。
insertion:
1. insert at last (com plete binary tree)
2. floot up to keep binary max tree
time complexity: O(log n)
範例如下,插入 node 17:
- 放在最後面,維持 complete binary tree
14
/ \
12 9
/ \ / \
4 8 8.5 17
- 逐項比大小,維持 binary max tree 性質
14
/ \
12 17
/ \ / \
4 8 8.5 9
17
/ \
12 14
/ \ / \
4 8 8.5 9
Heap v.s Array
Complete binary tree -> array
Heap tree -> partially ordered array
14 / \ 12 9 -> 14, 12, 9, 4, 8, 8.5 / \ / 4 8 8.5
Heap sort
假設已經有 array 與 heap
select sort on array: O(n^2)
n^2: O(n)次 * O(n)找select sort on heap: O(n*log n)
n*log n: O(n)次 * O(1)找 + O(log n)排
那建好一個 heap 要花多少力氣?
利用 insertion 建立 heap
建立力氣: O(n)insertion * O(log n) -> O(nlog n)
所以:
- 從 unordered arry 變成 heap: O(nlog n)
- 再從 heap 去 sort: O(nlog n)
Heap sort time complexity: O(nlog n)
