下面是 SocketCAN Librar 使用的介紹,完整程式碼請參考: kaka-lin/Notes/Network/canbus/can_examples
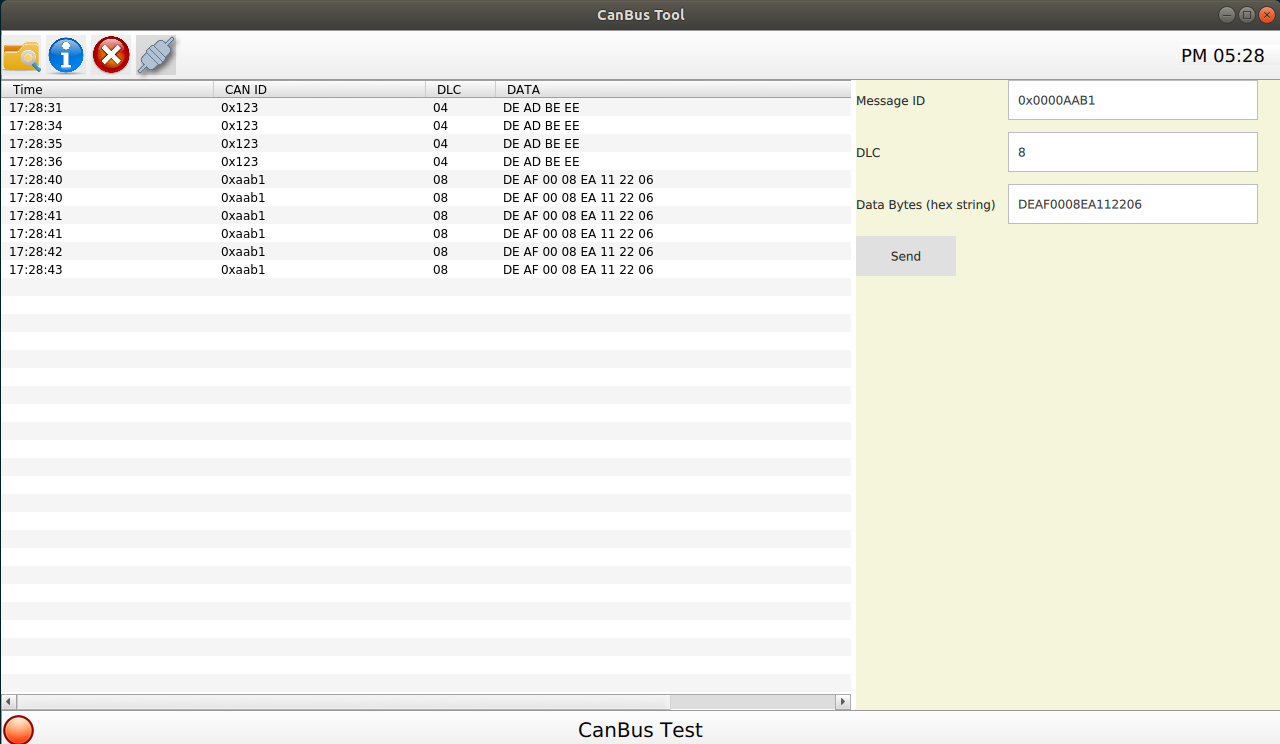
搭配 Qt 製作自己的 CanBus Tool 如下圖:

1. Create a CAN socket
The first step before doing anything is to create a socket.
int can_fd;
// PF_CAN or AF_CAN
if ((can_fd = socket(PF_CAN, SOCK_RAW, CAN_RAW)) < 0) {
perror("Error while Opening Socket");
return 1;
}
其中 socket() 的定義如下:
#include <sys/socket.h>
int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol)
domain: 選擇要用於通信的協議系列,常用的如下
AF_INET: IPv4 Internet protocolsAF_INET6: IPv6 Internet protocolsAF_CAN: Controller Area Network automotive bus protocol
type: Socket 的類型,常用的如下
SOCK_STREAM: Provides sequenced, reliable, two-way, connection-based byte streams. An out-of-band data transmission mechanism may be supported, likeTCPorFTP.SOCK_DGRAM: Supports datagrams (connectionless, unreliable messages of a fixed maximum length), likeUDP.SOCK_RAW: Provides raw network protocol access, likeCAN.
protocol: 與 Socket 一起使用的特定協議,如下
IPPROTO_TCPIPPTOTO_UDPCAN_RAW
2. Bind the socket to the CAN Interface:
Next, we must retrieve the interface index for the interface name (can0, can1, vcan0 etc) we wish to use. To do this we send an I/O control call and pass an ifreq structure containing the interface name:
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <net/if.h>
struct ifreq ifr;
strcpy(ifr.ifr_name, '"can0");
ioctl(can_fd, SIOCGIFINDEX, &ifr);
Then bind the socket to the CAN interface:
struct sockaddr_can addr;
memset(&addr, 0, sizeof(addr));
addr.can_family = AF_CAN;
addr.can_ifindex = ifr.ifr_ifindex;
if (bind(can_fd, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(addr)) < 0) {
perror("Error in Socket bind");
return 1;
}
3. Sending/Reading a frame
Sending a frame
To send a CAN frame, one must initialize a can_frame structure and populate it with data.
struct can_frame {
canid_t can_id; /* 32 bit CAN_ID + EFF/RTR/ERR flags */
__u8 can_dlc; /* frame payload length in byte (0 .. 8) */
__u8 __pad; /* padding */
__u8 __res0; /* reserved / padding */
__u8 __res1; /* reserved / padding */
__u8 data[8] __attribute__((aligned(8)));
};
To send a frame, initialize a can_frame with an ID of 0x123, a payload containing “0xDEADBE11” and send it using the write() system call:
#include <linux/can.h>
#include <linux/can/raw.h>
struct can_frame frame;
frame.can_id = 0x123;
frame.can_dlc = 4;
frame.data[0] = 0xDE;
frame.data[1] = 0xAD;
frame.data[2] = 0xBE;
frame.data[3] = 0x11;
if (write(can_fd, &frame, sizeof(struct can_frame)) != sizeof(struct can_frame)) {
perror("Write");
return 1;
}
Reading a frame
To read a frame, initialize a can_frame and call the read() system call. This will block until a frame is available.
int nbytes;
struct can_frame frame;
nbytes = read(can_fd, &frame, sizeof(struct can_frame));
if (nbytes < 0) {
perror("Read");
return 1;
}
printf("0x%03X [%d] ",frame.can_id, frame.can_dlc);
for (int i = 0; i < frame.can_dlc; i++)
printf("%02X ",frame.data[i]);
printf("\r\n");
4. Closing the socket
if (close(s) < 0) {
perror("Close");
return 1;
}
